Embark on a journey through the intricate world of ERP system integration, where businesses strive to harmonize their operations for optimal efficiency. This overview promises a blend of insight and practicality, offering a fresh perspective on the fusion of diverse systems within a cohesive framework.
Exploring the various integration methods and challenges, this discussion delves into the core of ERP system integration, shedding light on its significance in the modern business landscape.
Overview of ERP System Integration
ERP system integration involves connecting different software applications and systems within an organization to streamline data flow and improve overall efficiency. By integrating various systems, businesses can ensure that data is shared seamlessly across departments, enabling better decision-making and enhancing productivity.
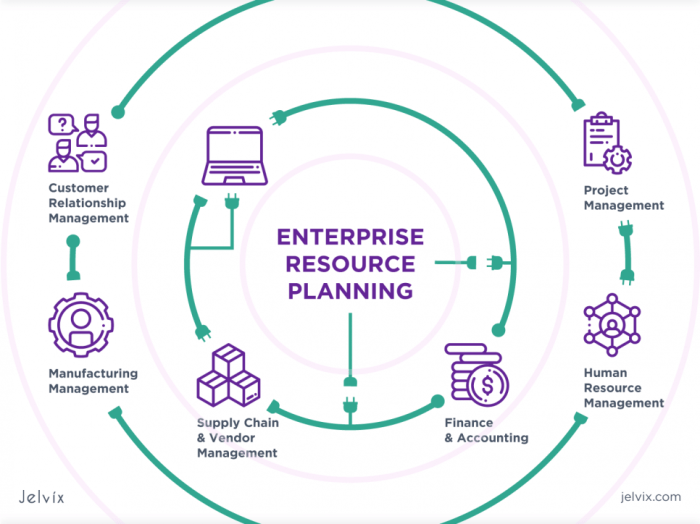
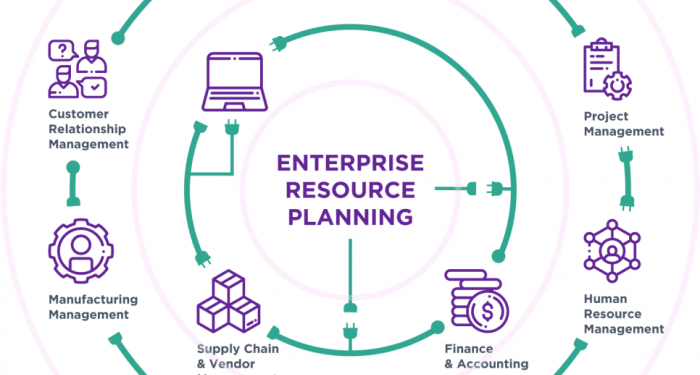
Systems Integrated with ERP
- Customer Relationship Management (CRM) systems: CRM systems are often integrated with ERP to provide a comprehensive view of customer interactions and streamline sales and marketing processes.
- Supply Chain Management (SCM) systems: Integrating SCM systems with ERP helps in optimizing inventory management, procurement, and logistics operations.
- Human Resources Management (HRM) systems: HRM systems integrated with ERP facilitate better management of employee data, payroll, and benefits administration.
- Business Intelligence (BI) systems: Integrating BI systems with ERP allows for advanced data analytics and reporting capabilities, enabling organizations to make data-driven decisions.
Importance of Seamless Integration
Seamless integration of systems is crucial for business operations as it ensures that data is consistent, accurate, and up-to-date across all platforms. This enables employees to access real-time information, collaborate effectively, and make informed decisions. Moreover, integrated systems eliminate the need for manual data entry and reduce the risk of errors, leading to improved productivity and cost savings for the organization.
Types of ERP System Integration
ERP system integration can be achieved through various methods, each offering unique benefits and drawbacks. Two common types of integration methods used in ERP systems are batch processing and real-time integration.
Batch Processing
Batch processing involves collecting data over a period of time and processing it in batches at a scheduled interval. The data is typically stored in a temporary location before being transferred to the ERP system for processing. This method is useful for non-time-sensitive tasks and can help optimize system resources by reducing the load on the ERP system during peak hours.
- Benefits of Batch Processing:
- Efficient use of system resources.
- Reduced impact on ERP system performance.
- Scheduled processing allows for better resource allocation.
- Drawbacks of Batch Processing:
- Data may not be up-to-date.
- Delayed processing can lead to outdated information.
- Not suitable for real-time decision-making.
Real-Time Integration
Real-time integration, on the other hand, involves immediate processing and updating of data in the ERP system as soon as it is received. This method ensures that information is always current and enables quick decision-making based on real-time data. However, real-time integration may require more system resources and can impact system performance during high-volume transactions.
- Benefits of Real-Time Integration:
- Up-to-date information for accurate decision-making.
- Immediate data processing for timely actions.
- Enhanced visibility and control over business processes.
- Drawbacks of Real-Time Integration:
- Higher system resource requirements.
- Potential impact on system performance during peak loads.
- Complex implementation and maintenance.
Common Challenges in ERP System Integration
When integrating ERP systems, businesses often encounter several common challenges that can hinder the process and impact overall efficiency. One of the key challenges is the complexity of merging different systems and processes into a unified platform.
Data Migration and Synchronization
One of the major challenges in ERP system integration is related to data migration and synchronization. This involves transferring data from legacy systems to the new ERP system while ensuring accuracy, consistency, and completeness. Issues such as data loss, duplication, and inconsistency can arise during this process, leading to disruptions in operations.
- Ensure Data Quality: To overcome data migration challenges, businesses should conduct a thorough data cleansing process to identify and rectify any errors or inconsistencies in the data before migration.
- Implement Data Mapping: Developing a detailed data mapping strategy can help in mapping data fields between the legacy systems and the new ERP system, ensuring seamless data transfer and synchronization.
- Test Data Integration: Performing rigorous testing of data integration processes is essential to identify and resolve any issues before full implementation. This helps in minimizing the risk of data discrepancies and ensuring data accuracy.
Best Practices for Successful ERP System Integration
When it comes to integrating an ERP system with your existing infrastructure, following best practices is crucial for a smooth and successful implementation. Here are some key guidelines to consider:
Thorough Planning and Execution
- Start by clearly defining the objectives and scope of the integration project.
- Involve key stakeholders from different departments to ensure all requirements are considered.
- Develop a detailed project plan with clear timelines and milestones.
Importance of Testing and Quality Assurance
- Conduct thorough testing at each stage of the integration process to identify and address any issues early on.
- Implement quality assurance measures to ensure that data is accurately transferred and processed.
- Perform user acceptance testing to validate that the integrated system meets the business needs.
Data Accuracy and Consistency
- Establish data mapping processes to ensure that information is mapped correctly between systems.
- Implement data validation checks to verify the accuracy and completeness of data during the integration.
- Regularly monitor data integrity post-integration to maintain consistency and reliability.
End of Discussion
In conclusion, the realm of ERP system integration emerges as a critical domain for businesses seeking to streamline their processes and enhance productivity. By embracing best practices and overcoming challenges, organizations can harness the power of integration to propel their operations towards success.
FAQ Insights
What are the key benefits of ERP system integration?
ERP system integration enables seamless data flow between different systems, streamlining operations and improving overall efficiency.
How can businesses ensure data accuracy during integration processes?
By conducting thorough testing and quality assurance measures, businesses can maintain data accuracy and consistency throughout the integration process.
What is the significance of real-time integration compared to batch processing?
Real-time integration allows for instant data updates and decisions, offering a more responsive and agile approach compared to batch processing.





![Best Construction ERP Software [2024 Edition]](https://health.bandungnews.id/wp-content/uploads/2025/10/Top-10-Best-Construction-ERP-Software-to-Use-in-2024-1-120x86.jpg)



