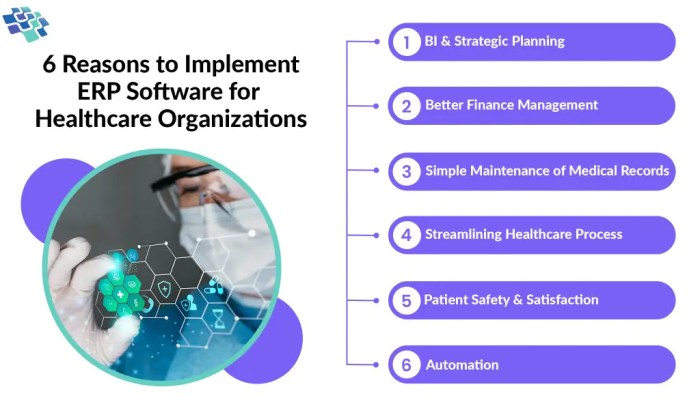
As we delve into the realm of healthcare ERP, we uncover a world where technology revolutionizes the way healthcare operates. From streamlining processes to enhancing patient care, healthcare ERP systems play a pivotal role in shaping the future of the industry.
Let's embark on a journey to explore the key aspects of these innovative solutions.
Introduction to Healthcare ERP
Healthcare ERP, or Enterprise Resource Planning, is a software system designed specifically for the healthcare industry to streamline processes, improve efficiency, and enhance overall patient care. It integrates various functions such as financial management, human resources, supply chain management, and patient data into one centralized platform.
Implementing a Healthcare ERP system offers numerous benefits to healthcare organizations, including increased productivity, reduced costs, improved decision-making capabilities, better resource allocation, enhanced data security, and compliance with regulations.
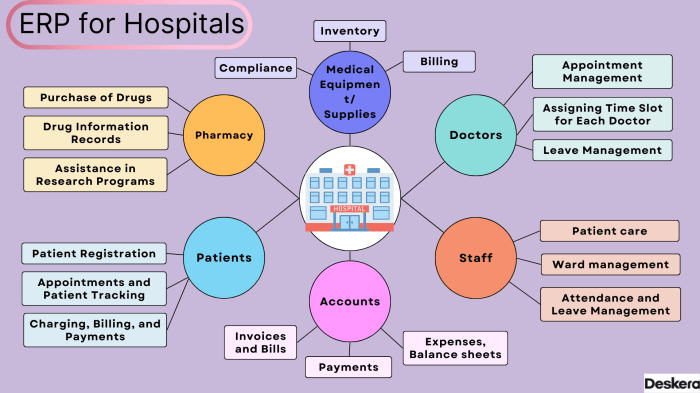
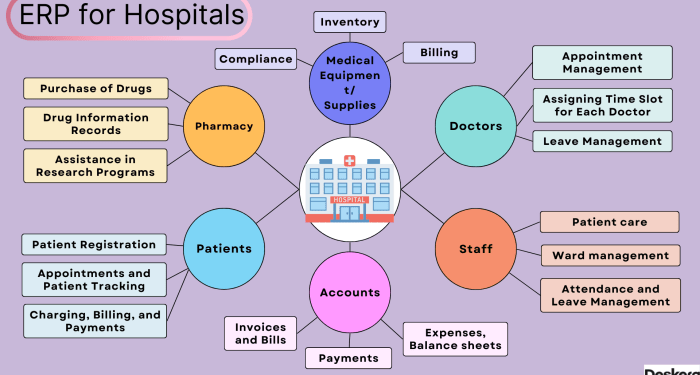
Key Features of Healthcare ERP Solution
- Centralized Data Management: Allows healthcare providers to access and update patient records, schedules, and other critical information in real-time from a single platform.
- Financial Management: Helps in managing billing, invoicing, and financial transactions efficiently, ensuring accurate revenue tracking and reporting.
- Inventory Management: Enables healthcare facilities to track and manage inventory levels, reduce waste, and ensure timely availability of medical supplies.
- HR Management: Streamlines human resource processes such as payroll, employee scheduling, performance evaluations, and training, leading to improved staff satisfaction and retention.
- Reporting and Analytics: Provides comprehensive reporting tools and analytics to track key performance indicators, identify trends, and make data-driven decisions for better patient outcomes.
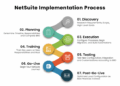
Implementation of Healthcare ERP
Implementing a Healthcare ERP system in an organization involves several crucial steps that need to be carefully planned and executed to ensure a successful transition. From initial planning to training and ongoing support, each stage plays a vital role in the overall implementation process.
Steps involved in implementing a Healthcare ERP system:
- Assessment and Planning: Conduct a thorough assessment of the organization's current processes and identify key areas where an ERP system can bring improvements. Develop a detailed plan outlining the goals, timelines, and resources required for implementation.
- Vendor Selection: Research and evaluate different ERP vendors to find the one that best fits the organization's needs. Consider factors such as system compatibility, scalability, and customer support before making a decision.
- Customization and Configuration: Work closely with the chosen vendor to customize the ERP system to align with the organization's unique workflows and requirements. Configure the system settings, modules, and functionalities accordingly.
- Data Migration: Transfer existing data from legacy systems to the new ERP platform while ensuring data integrity and accuracy. Develop a data migration strategy to minimize disruptions during the transition.
- Training and Testing: Provide comprehensive training to staff members on how to use the new ERP system effectively. Conduct thorough testing to identify and address any issues or bugs before fully implementing the system.
- Go-Live and Support: Launch the ERP system in a phased approach to minimize disruptions to daily operations. Provide ongoing support and maintenance to address any issues that may arise post-implementation.
Challenges faced during Healthcare ERP implementation:
- Resistance to Change: Employees may resist adopting new technologies and processes, leading to decreased productivity and efficiency.
- Integration Issues: Ensuring seamless integration with existing systems and technologies can be complex and challenging.
- Data Security Concerns: Safeguarding sensitive patient information and complying with regulatory requirements pose significant challenges during implementation.
- Budget Constraints: Limited financial resources may impact the organization's ability to invest in a comprehensive ERP solution.
Examples of successful Healthcare ERP implementation stories:
One notable success story is a large hospital network that implemented a comprehensive ERP system, resulting in streamlined operations, improved patient care, and increased cost savings. The organization saw a significant reduction in administrative tasks and enhanced data accuracy, leading to better decision-making and overall efficiency.
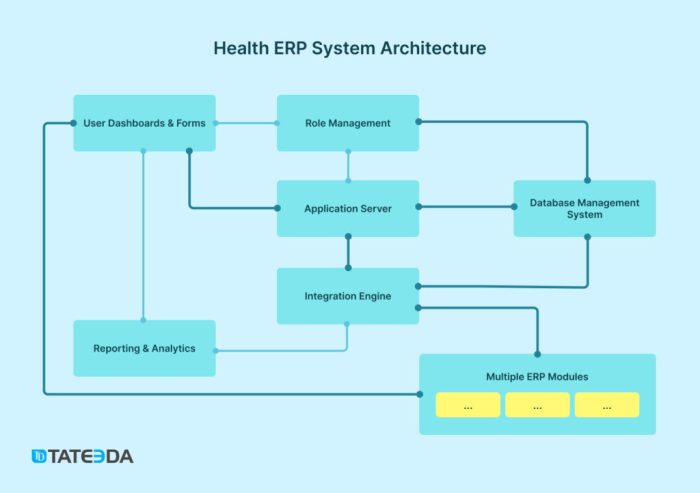
Integration with Existing Systems
Integrating Healthcare ERP with existing systems in a healthcare facility is crucial for streamlining operations and improving overall efficiency.
Comparison of Integration Methods
- API Integration: This method involves using Application Programming Interfaces to connect the Healthcare ERP system with other existing systems, allowing for seamless data exchange.
- Middleware Integration: Middleware software acts as a bridge between different systems, facilitating communication and data sharing between the Healthcare ERP and existing systems.
- Database Integration: Integrating databases of different systems enables real-time access to information across platforms, enhancing decision-making processes.
Impact on Operational Efficiency and Patient Care
Seamless integration of Healthcare ERP with existing systems leads to improved operational efficiency by reducing manual data entry, minimizing errors, and increasing data accuracy. This, in turn, enhances patient care by providing healthcare providers with timely and accurate information, leading to better diagnosis and treatment outcomes.
Data Security and Compliance
Data security and regulatory compliance are crucial aspects of any Healthcare ERP system to ensure the protection of sensitive patient information and adherence to industry standards.
Measures for Data Security
- Encryption of data at rest and in transit to prevent unauthorized access.
- Role-based access control to restrict data access based on user roles and responsibilities.
- Regular security audits and penetration testing to identify vulnerabilities and strengthen defenses.
- Implementation of data backup and disaster recovery plans to prevent data loss.
Regulatory Compliance Requirements
- Compliance with HIPAA (Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act) regulations to protect patient privacy and security.
- Adherence to GDPR (General Data Protection Regulation) for data protection and privacy of European Union residents.
- Meeting HITECH (Health Information Technology for Economic and Clinical Health Act) requirements for electronic health records security.
Consequences of Non-Compliance
- Financial penalties and legal consequences for violations of data security and privacy regulations.
- Loss of trust and reputation among patients and stakeholders due to breaches of sensitive information.
- Potential civil and criminal charges for negligence in protecting patient data.
Customization and Scalability
Customization and scalability are crucial aspects of Healthcare ERP systems that allow organizations to tailor the software to their specific needs and ensure it can grow along with the organization.
Customization Options in Healthcare ERP Systems
- Healthcare ERP systems offer a range of customization options, allowing organizations to configure workflows, data fields, and reports to align with their unique processes and requirements.
- For example, a hospital may customize the patient registration module to capture specific information relevant to their specialty, such as allergies or previous surgeries.
- Customization also extends to user roles and permissions, ensuring that only authorized personnel have access to sensitive patient data.
Scalability of Healthcare ERP Systems
- Healthcare ERP systems are designed to scale with the organization, accommodating growth in patient volume, services offered, and number of facilities.
- As organizations expand, they can add new modules, features, and integrations to their ERP system without disrupting existing operations.
- Scalability also ensures that Healthcare ERP systems can handle increased data processing requirements and user loads as the organization grows.
User Training and Support
User training and ongoing support are crucial elements in ensuring the successful implementation and utilization of a Healthcare ERP system within a healthcare organization. Proper training programs and continuous support contribute to the efficiency and effectiveness of the system, ultimately benefiting patients and healthcare providers alike.
Training Programs
Implementing a Healthcare ERP system requires comprehensive training programs for healthcare staff to ensure they can effectively navigate and utilize the system. Training should cover all aspects of the ERP system, including data entry, reporting, and system maintenance. Hands-on training sessions, workshops, and online tutorials can help users become familiar with the system and its functionalities.
Regular refresher courses should also be provided to keep users up-to-date with any system updates or changes.
Ongoing Support
Ongoing support plays a critical role in maintaining the performance of a Healthcare ERP system. Organizations should have dedicated support teams or help desks to address any issues or concerns that users may encounter while using the system. Timely assistance and troubleshooting can prevent downtime and ensure uninterrupted access to critical patient information.
Regular system audits and performance evaluations can help identify areas for improvement and optimize system functionality.
User Adoption and Satisfaction
To ensure user adoption and satisfaction with the Healthcare ERP solution, organizations should focus on clear communication, feedback mechanisms, and continuous improvement. Engaging users in the implementation process, soliciting feedback, and addressing user concerns can help promote system acceptance and usage.
Providing incentives for system utilization, recognizing user achievements, and offering ongoing training opportunities can also boost user satisfaction and engagement with the system.
Final Wrap-Up

In conclusion, healthcare ERP systems stand as a beacon of efficiency and effectiveness in the healthcare landscape. By embracing these advanced technologies, organizations can elevate their operations and ultimately improve patient outcomes. The future of healthcare lies in the seamless integration and customization offered by ERP systems, paving the way for a brighter and more streamlined industry.
FAQ Corner
How can Healthcare ERP systems benefit healthcare organizations?
Healthcare ERP systems can improve operational efficiency, streamline processes, enhance data security, and ultimately lead to better patient care outcomes.
What are the key challenges faced during the implementation of Healthcare ERP systems?
Challenges may include resistance to change, data migration issues, training requirements, and ensuring seamless integration with existing systems.
Why is data security crucial in Healthcare ERP systems?
Data security is vital to protect sensitive patient information and maintain regulatory compliance, safeguarding against potential breaches and cyber threats.
How customizable are Healthcare ERP solutions?
Healthcare ERP systems offer varying levels of customization to tailor the software to meet specific organizational needs, ensuring optimal functionality and efficiency.
What role does user training play in the successful implementation of Healthcare ERP systems?
User training is essential to ensure healthcare staff can effectively utilize the ERP system, maximizing its benefits and enhancing overall performance.





![Best Construction ERP Software [2024 Edition]](https://health.bandungnews.id/wp-content/uploads/2025/10/Top-10-Best-Construction-ERP-Software-to-Use-in-2024-1-120x86.jpg)



